 The review is based on the materials of the 2023 Billion-Ton Report: An Assessment of U.S. Renewable Carbon Resources, published by the US Department of Energy in March 2024. This report assesses the potential of renewable biomass resources to support the US Department of Energy’s goals of replacing fossil fuels with renewable, biogenic carbon resources that, if managed effectively, have a lower climate impact.
The review is based on the materials of the 2023 Billion-Ton Report: An Assessment of U.S. Renewable Carbon Resources, published by the US Department of Energy in March 2024. This report assesses the potential of renewable biomass resources to support the US Department of Energy’s goals of replacing fossil fuels with renewable, biogenic carbon resources that, if managed effectively, have a lower climate impact.
In 2022, bioenergy became the largest source of renewable energy in the United States, accounting for approximately 5% of the country’s energy production. Demand for renewable fuels is growing, especially in the aviation, marine and rail transport sectors. Let’s consider in more detail the current state of the US energy industry and trends in the energy use of biomass.
Consumption of primary energy
In the USA, since 2014, primary energy consumption has decreased by 0.5% (from 100.5 to 100.0 EJ[1]). It peaked at 102.8 EJ in 2018, followed by a decline in total primary energy consumption (TPE) in 2020 and 2021, mainly due to reduced fossil fuel use during the COVID-19 pandemic (Figure 2.1). From 2014 to 2022, coal consumption decreased by approximately 45% (from 19.0 to 10.3 EJ), and natural gas consumption increased by approximately 21.9% (from 28.9 to 35.2 EJ). These changes occurred as coal-fired power generation was phased out and replaced by renewables and natural gas. In 2022, the share of renewable energy sources in the energy sector was more than 8%.
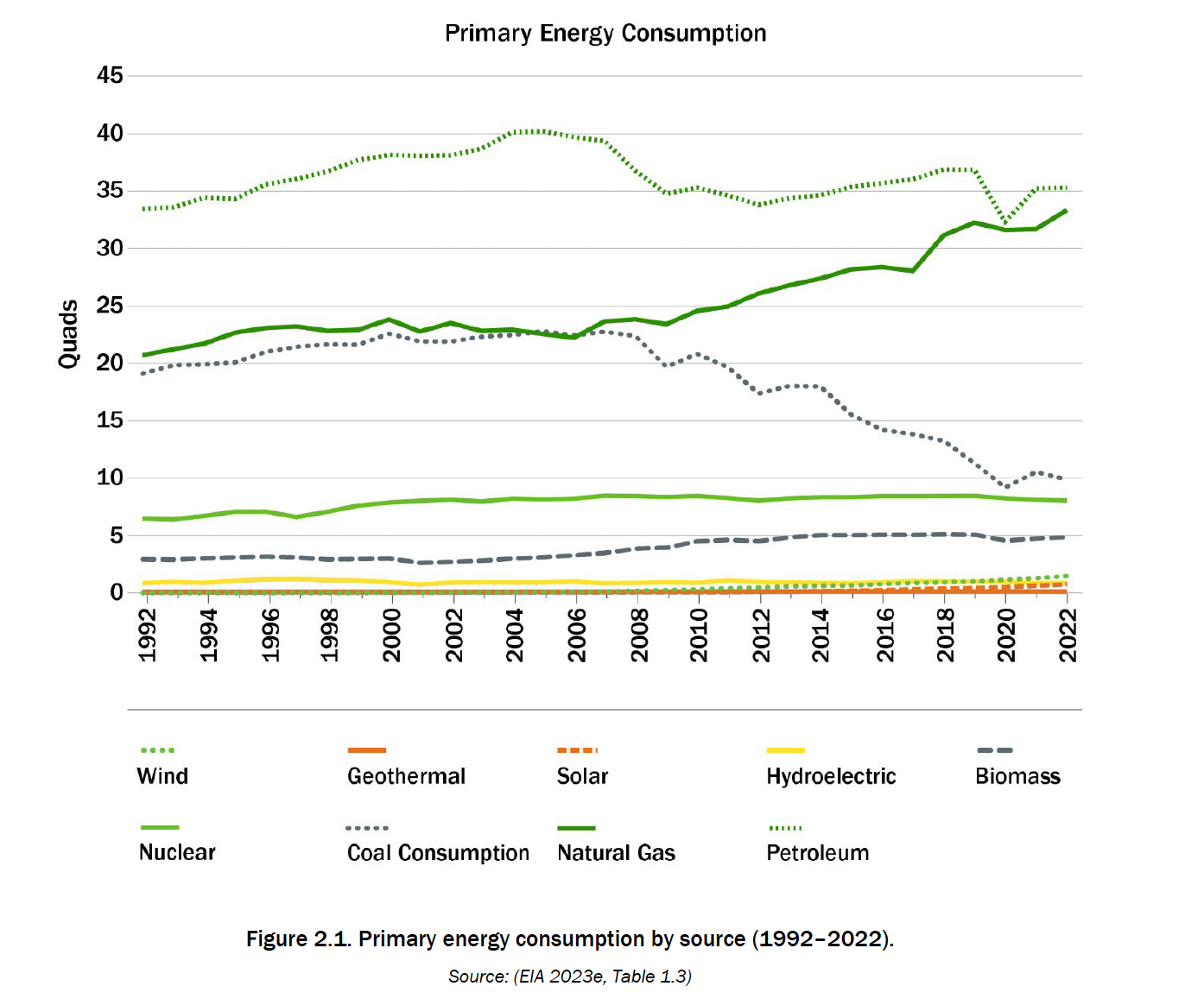
Since 2014, total energy consumption from renewable sources has increased by 19% (from 7.2 to 8.5 EJ) (Figure 2.2), while energy consumption from fossil fuels has decreased by about 2% (from 84.4 to 82.8 EJ). In 2022, biofuels were the largest single category of renewable energy sources with 30% of total RES consumption (2.5 EJ), followed by wood energy at 24.5% (2.1 EJ), wind at 18.3% ( 1.6 EJ), hydro – 11.1% (0.9 EJ), solar – 9.4% (0.8 EJ), waste – 5.1% (0.4 EJ) and geothermal – 1.5 % (0.1 EJ). The increase in the consumption of renewable energy was due to the increase in the consumption of wind energy (140%, 0.9 EJ) and solar energy (373%, 0.6 EJ). In 2022, biomass-based RES accounted for 60% (5.1 EJ) of total RES consumption.
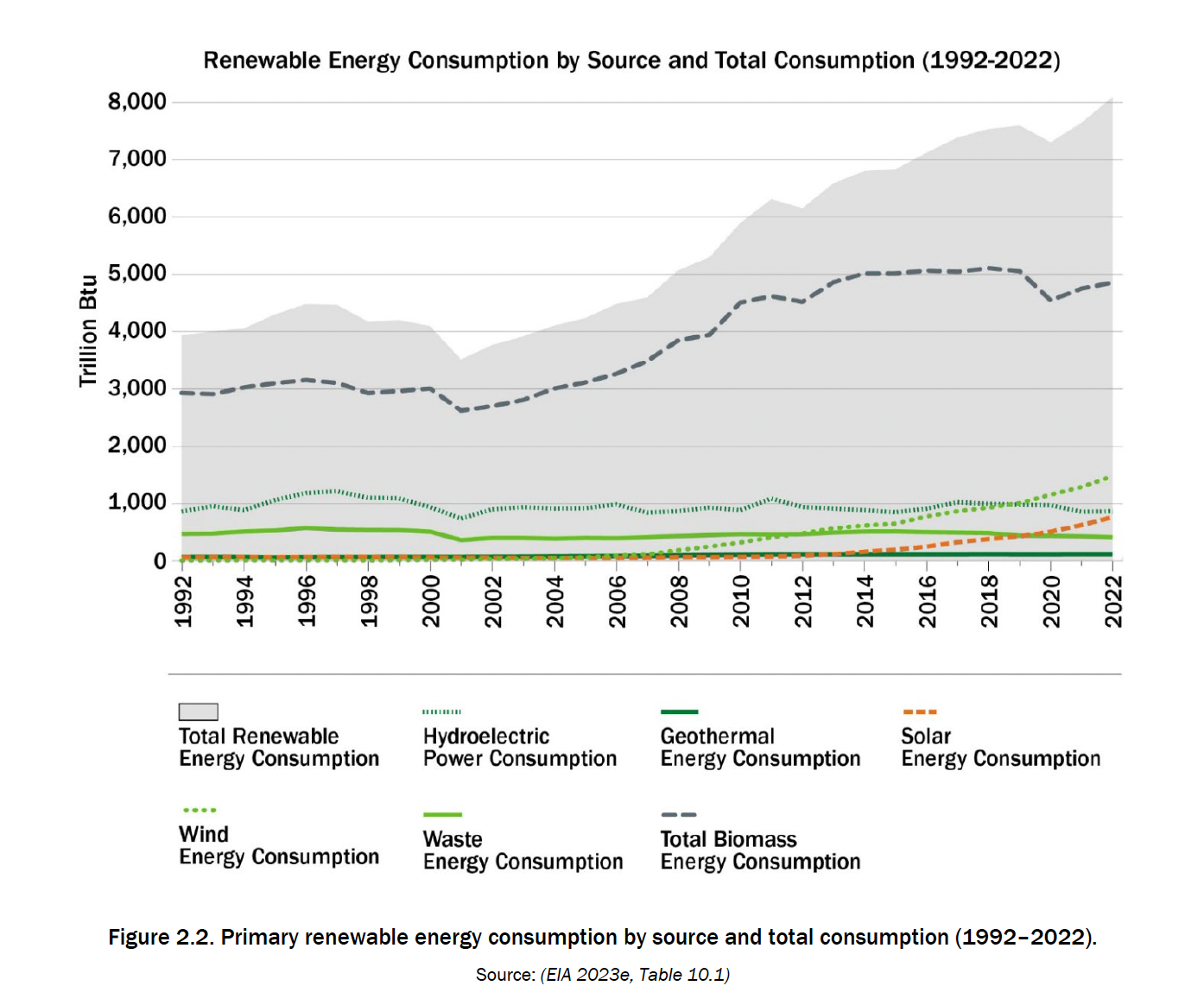
The following sections provide an overview of the bioenergy sector in the US by the categories of biofuels for transportation, heat, and electricity.
Biofuel for transport
In 2022, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) estimates that 18.7 billion gallons[2] of biofuels will be produced and about 17.6 billion gallons consumed. Renewable energy sources account for 5.7% of energy consumption by the US transportation sector. U.S. domestic production of biofuels in 2022, according to the EIA, increased by 18.5% compared to reported values in 2014. Bioethanol production increased by 7.4% and biodiesel – by 26.8%. There is a more rapid increase in production of advanced types of biofuels due to the introduction and development of their technologies. Thus, according to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), in 2022, compared to 2014, the growth in production volumes of renewable diesel fuel amounted to 813%, renewable jet fuel/solid aviation fuel (SAF) – 912%, gasoline blending component /bio-oil – 424%, biogas and other renewable gases – 1100%. In the Table 2.2 you can see summarized data on the domestic production of various types of biofuels in the USA in 2022.
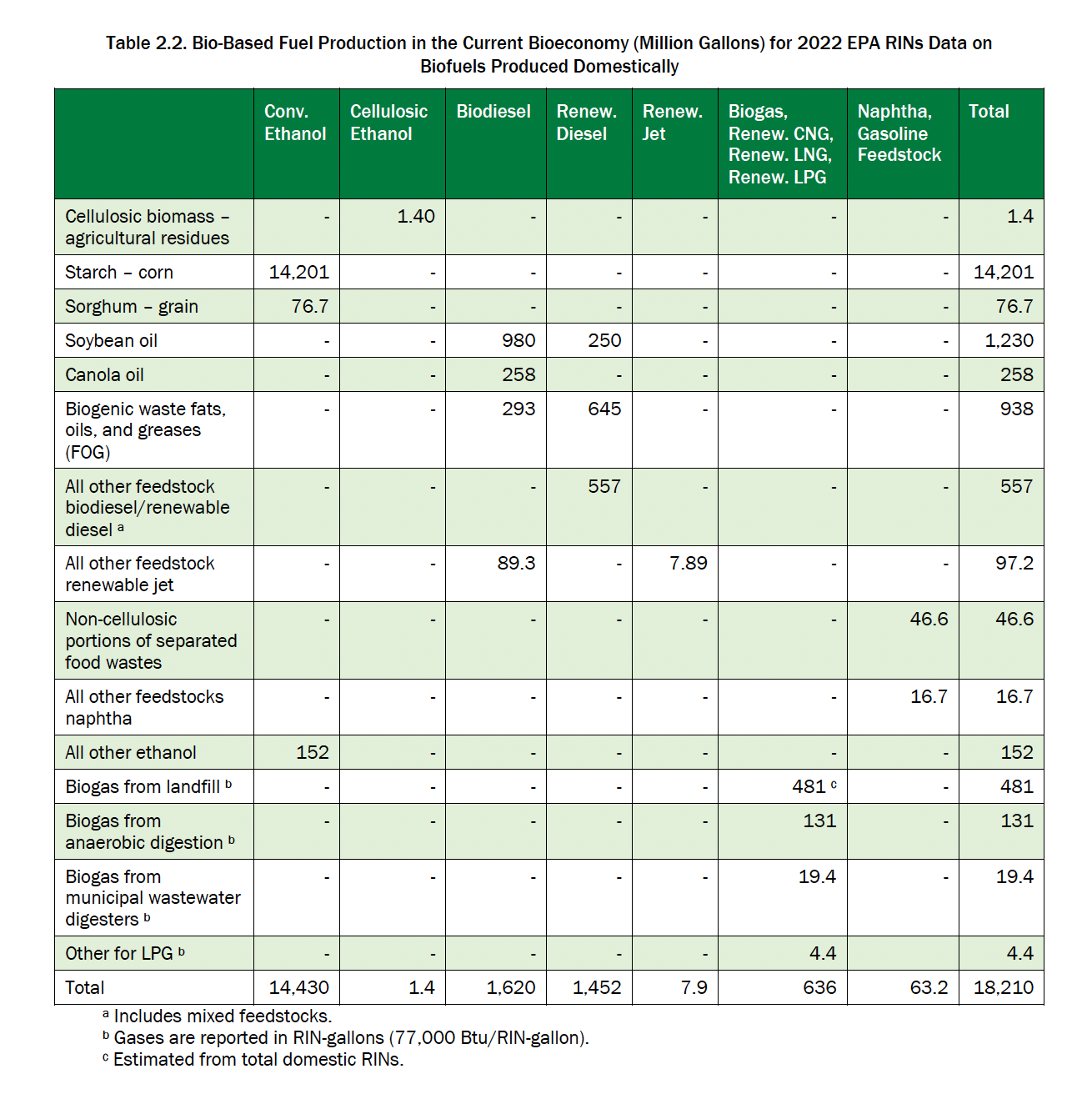
According to the EIA, fuel ethanol production was 15.4 billion gallons, and its consumption in the transportation sector was 14.0 billion gallons, where most of the fuel ethanol is blended with motor gasoline (finished). The main raw material for the production of ethanol is corn for grain, which accounted for 98% of the total mass of raw materials. In addition, in 2022, 1.7 million tons of sorghum grain was used for ethanol production. According to EPA reports, cellulosic ethanol production increased from 0.0007 billion gallons in 2014 to 0.0014 billion gallons in 2022.
Biologic diesel fuel is also called as biodiesel and renewable diesel. International standard ASTM D6751 defines biodiesel as fatty acid methyl ester. Renewable diesel fuel is produced with properties chemically equivalent to petroleum-derived diesel fuel and meets the ASTM D975 standard. Biodiesel is the second-largest biofuel in the U.S. after fuel ethanol, and renewable diesel is third. In 2022, according to the EIA, domestic biodiesel production was 1.62 billion gallons and consumption was 1.66 billion gallons of biodiesel, representing 8.2% of biofuel consumption. 3.6 million tons of soybean oil were used for the production of biodiesel. Soybean oil accounts for over 50% of all biodiesel RINs, followed by biogenic waste FOG at 16% and canola oil at 14%. In 2022, 1.5 billion gallons of renewable diesel fuel were produced and 1.7 billion gallons were consumed. 1.7 million tons of soybean oil were used at renewable diesel plants.
In 2022, 15.8 million gallons of renewable jet fuel were produced, of which 7.89 million gallons were domestically produced and 7.93 million gallons were foreign. At the time of writing of this report, there is only one North American producer of commercial renewable jet fuel operating with a plant in California based on the HEFA (hydrotreated esters and fatty acids) process using agricultural fats and waste oils. In 2022, the US Department of Energy, US Department of Transportation, and USDA launched a memorandum of understanding and roadmap, setting SAF production goals of 3 billion gallons per year by 2030 and 35 billion gallons per year by 2050.
Renewable biogas is renewable LNG (mainly methane), renewable LPG (methane) and renewable LPG. At the beginning of 2023, 93 dairy farms had digesters producing biogas for end use as LNG, as well as additional pipeline gas operations. In 2022, according to the EPA, 546 million RIN-equivalent gallons of renewable biogas were produced, of which about 74% came from landfills. In addition, 84.1 million gallons of recoverable LNG, which was almost entirely landfilled, and about 4.4 million RIN-equivalent gallons of LPG were produced.
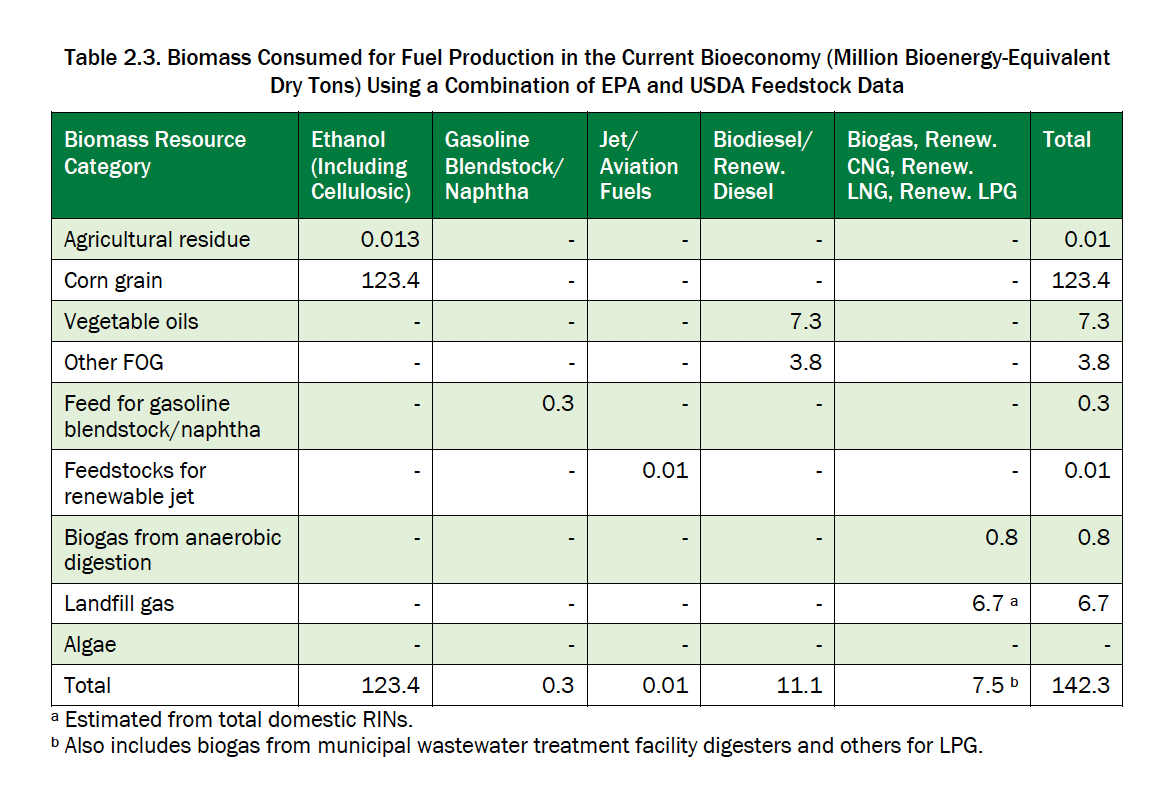
The assessment of the use of raw materials for the production of biofuels according to the data of the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) and EPA is presented in the Table 2.3.
Heat and electricity from biomass
Biomass is an important form of renewable energy for the production of heat and electricity in the United States, especially in industry. Household solid waste, landfill gas and wood biomass are used in power generation. In addition, thermal and electrical energy is produced from wood biomass in small community installations.
About 1.2% of annual US energy consumption comes from wood and wood waste (bark, sawdust, wood chips, wood scrap, and paper mill waste). Comparing recent data, electricity production from wood/wood waste has decreased from 0.4 EJ in 2014 to 0.3 EJ in 2022, and heat production from wood/wood waste has decreased from 1.6 EJ in 2014. to 1.3 EJ in 2022. The reduction in heat and electricity production from wood/wood waste is caused by the closure of pulp and paper mills.
Manure is collected and processed by anaerobic fermentation into biogas. Data from the AgSTAR database for 2023 indicate the operation of 250 anaerobic digestion facilities in the United States, producing heat and electricity, consuming 2.7 million tons (dry matter) of manure, which is 42% more than the 2016 Billion-ton Report (BT16). The total energy production in anaerobic reactors (biofuel and production of thermal and electrical energy) increased by 230% (from 1.9 to 3.5 million tons of dry matter per year).
In the Table 2.4 [3] presents data on biomass self-energy consumed for the production of heat and electricity in the United States for the electric power, industrial, commercial and residential sectors in 2022. The results of the conversion of this biomass energy into tons of raw materials consumed for the production of heat and electricity by sector given in the Table 2.5.
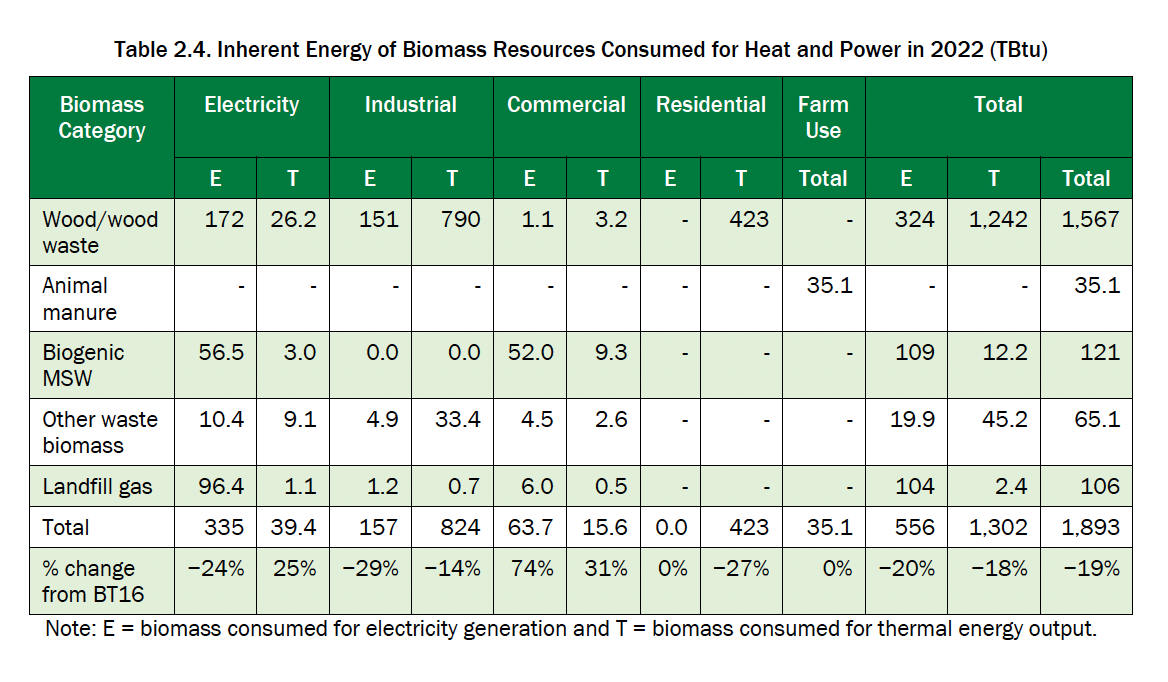
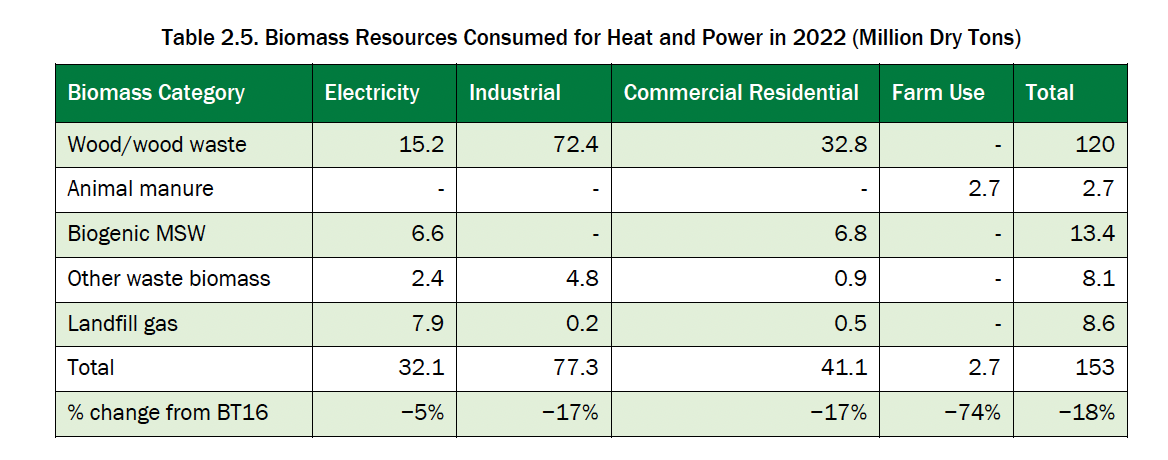
Total volumes of biomass consumption for the energy industry
The total consumption of biomass resources for obtaining energy, in particular transport, electricity and heat, is given in the Table 2.6. Compared to the BT16 report, the total annual biomass currently consumed for the production of biofuels for transport and heat and electricity has decreased by 18 million tons (6%). At the same time, the production of biofuels increased by 19%, consuming an additional 16 million tons of raw materials annually (11%), while the biomass used for the production of heat and electricity decreased by 35 million tons per year (19%), and the use of landfill gas increased by 36%. The main sources of biomass in the current US bioeconomy remain corn kernels for the production of biofuels for transportation and forestry/wood and wood waste for the production of heat and electricity. In total, in 2022, 342 tons of dry matter of biomass were used for energy needs.
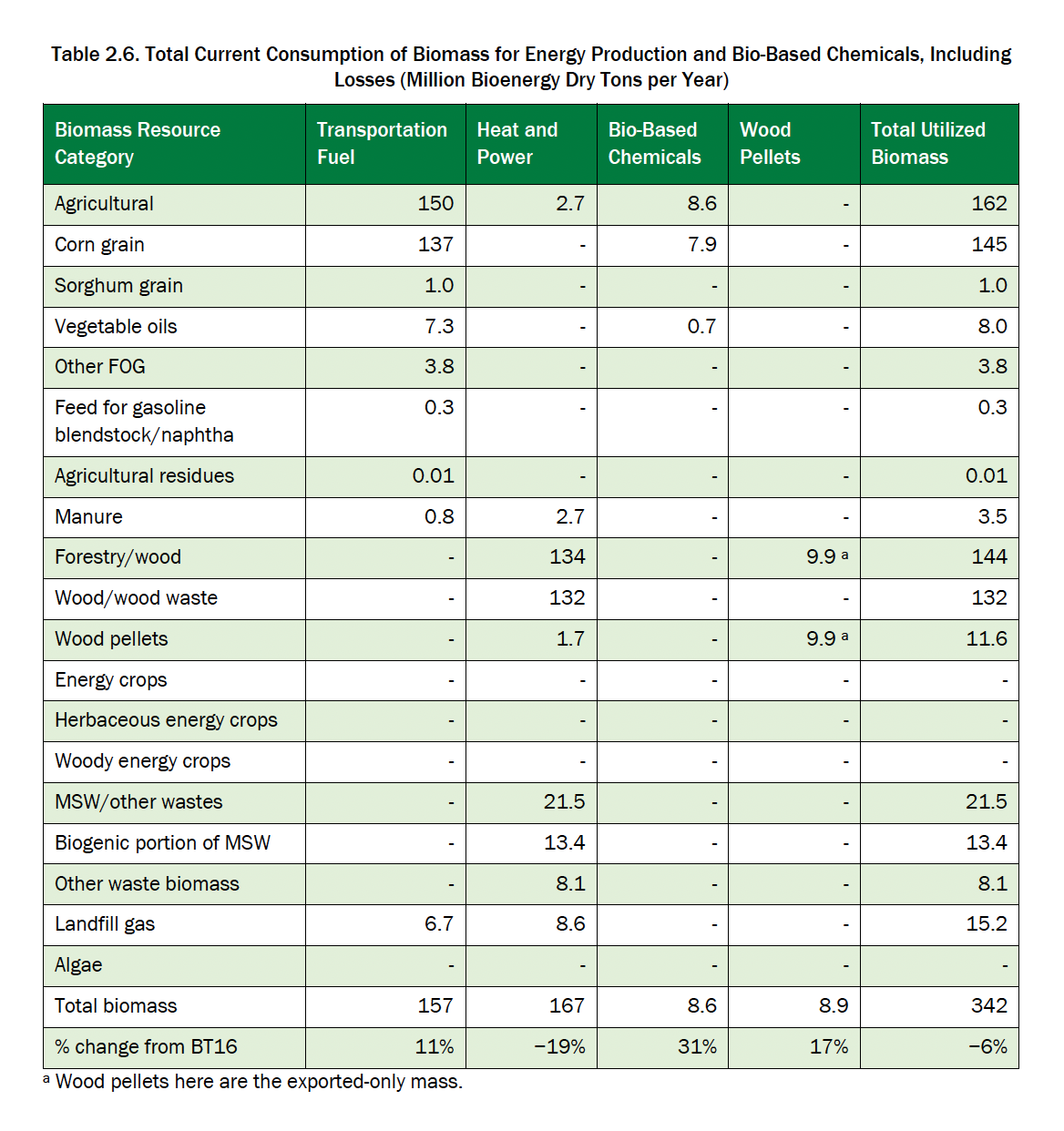
In the near future, the resources can ensure an increase in the actual use of biomass to about 627 million tons of dry matter per year, which would roughly double the current economics of the US bioenergy sector. The resources of the mature market can provide approximately 1,026–1,361 million tons of biomass (dry matter) per year, in particular due to the involvement of energy crops and intermediate oil crops. Also, the authors of the report see the cultivation of algae for energy as promising. In the Table ES-2 [4] presents the results of the evaluation of biomass potential in the USA under different scenarios.
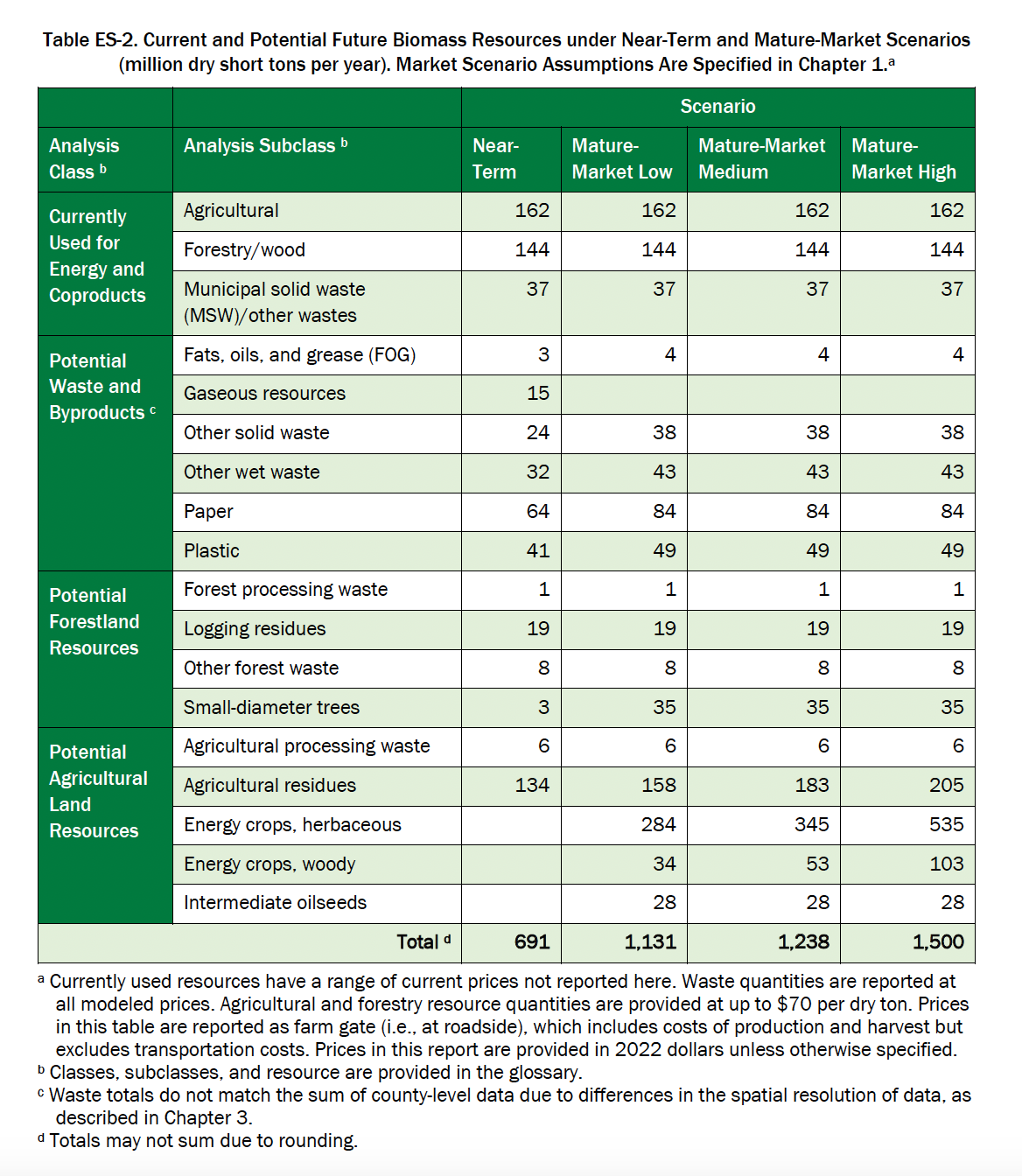
[1] Quad is the unit of measurement of primary energy consumption in the text of the original report. 1 quad = quadrillion (1015) British thermal units (BTU) = 1.055×1018 J = 1.055 EJ 1 BTU = 1.055 kJ
[2] 1 gallon = 3.785 liters
[3] In the original report, the table data are given in TBTU. The ratio was used for the calculation: 1 TBTU = 1.055 ∙ 1015 J = 1.055 PJ
[4] In the original report, the data are given in million short tons of dry matter. To convert to metric tons of dry matter the ratio 1 US short ton = 0.9071847 metric tons is used
The full text of the 2023 Billion-Ton Report: An Assessment of U.S. Renewable Carbon Resources can be found at: https://www.energy.gov/eere/bioenergy/2023-billion-ton-report-assessment-us-renewable-carbon-resources.
This analysis was prepared for SAF Ukraine by Semen Drahniev, an expert of the Bioenergy Association of Ukraine.