 On June 21, 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released a finalized version of the 2023, 2024, and 2025 Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) to strengthen U.S. energy security, support U.S. rural economy, and expand production of low-carbon fuels.
On June 21, 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released a finalized version of the 2023, 2024, and 2025 Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) to strengthen U.S. energy security, support U.S. rural economy, and expand production of low-carbon fuels.
The final rule establishes a balanced increase in biofuel consumption from 2023 to 2025, reducing dependence on oil imports by about 130,000 to 140,000 barrels per day during this period. The estimated value of energy security benefits to the US economy ranges from $173 to $192 million per year.
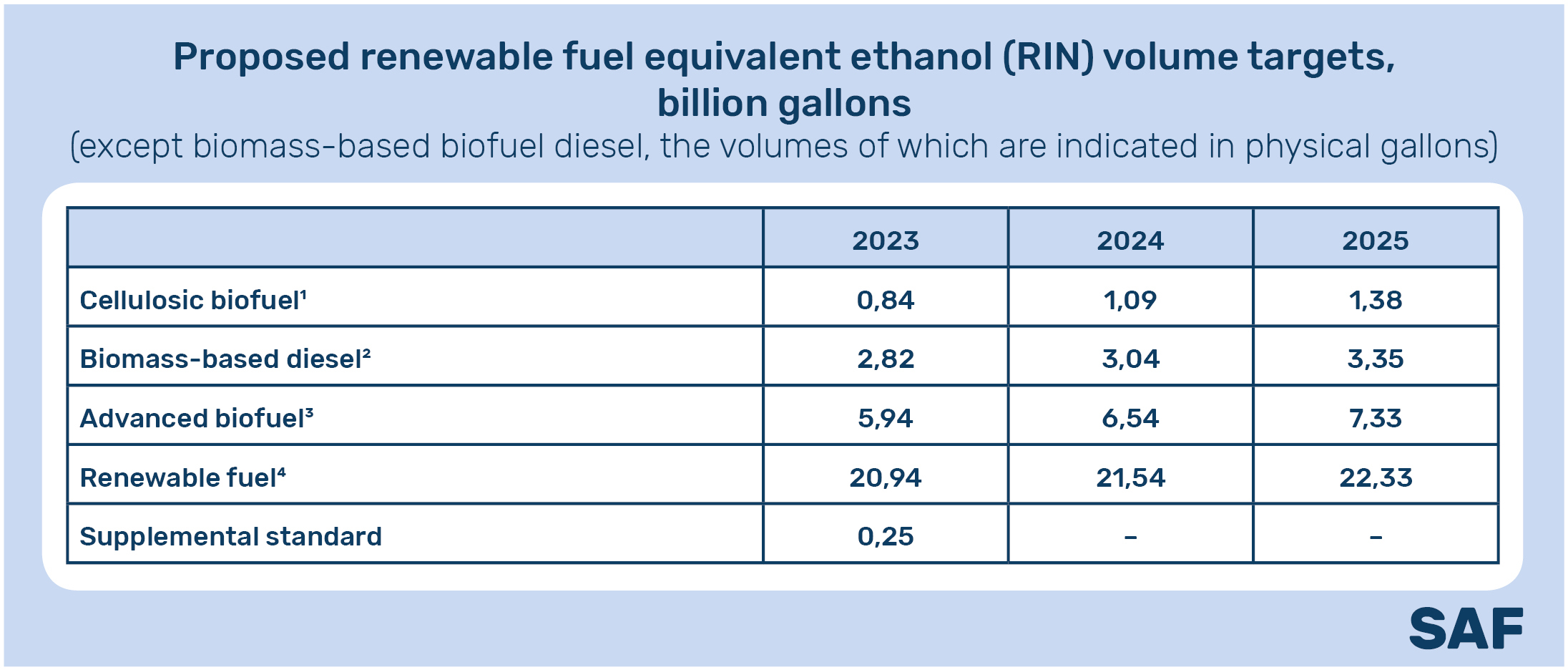
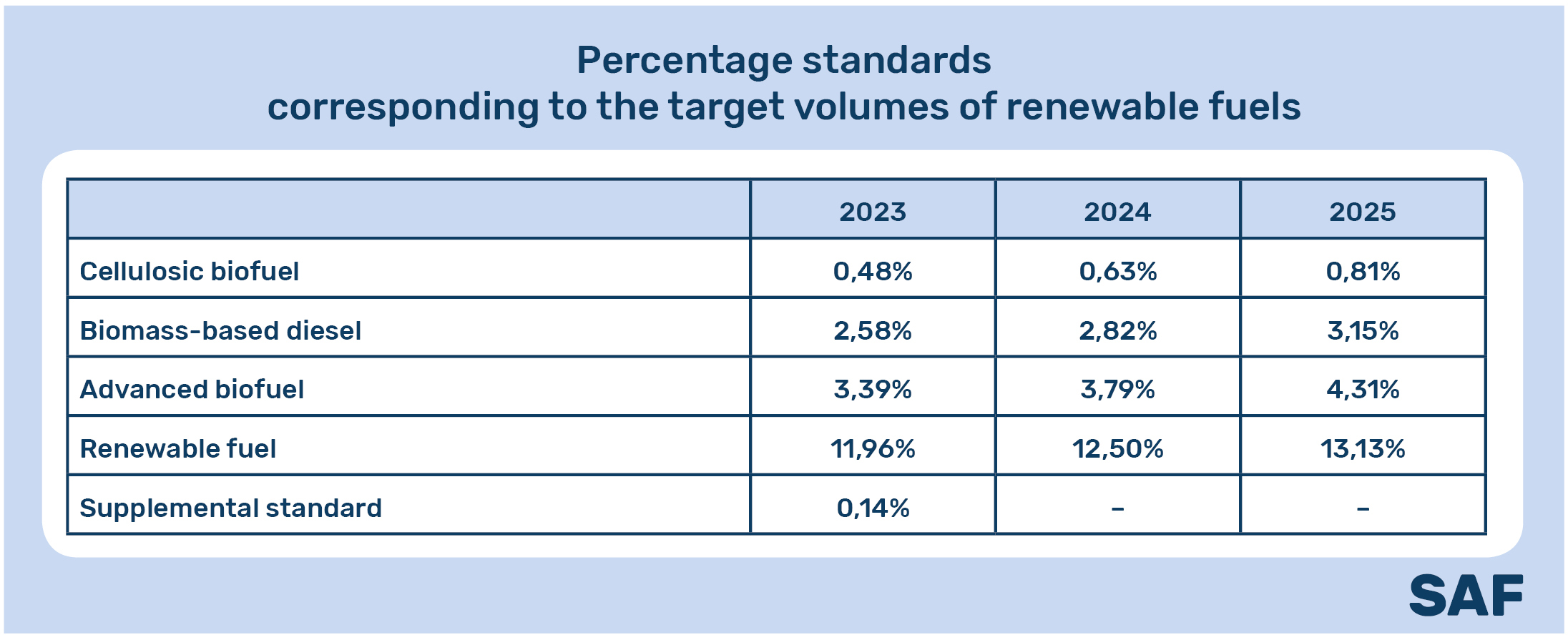
The rule sets applicable volume and percentage targets for 2023 through 2025 for cellulosic biofuels, biomass-based diesel, advanced biofuels, and total renewable fuels that U.S. refiners must annually blend with gasoline and diesel. In addition, several regulatory changes have been made to the Renewable Fuel Standard programme, including changes related to the use of biogas.
EPA’s final rule includes a total renewable fuel commitment of 20.94 billion gallons (≈75.7 billion liters) by 2023, of which 15 billion gallons (≈56.78 billion liters) will come from conventional renewable fuels , for example, ethanol from corn, which is slightly less than the previously proposed volumes of 15.25 billion gallons (≈ 57.73 billion liters). The rule also provides for an additional 250 million gallons (≈ 946.25 million liters) volume requirement in 2023 to make up for illegally canceled volumes in 2016.
In 2024 and 2025, the final EPA requirements set renewable fuel volumes at 21.54 billion gallons (≈ 81.53 billion liters) and 22.33 billion gallons (≈ 84.52 billion liters), respectively. The conventional renewable fuel requirement is 15 billion gallons (≈56.78 billion liters) for each of these years.
Note
1 Cellulosic biofuel means renewable fuel derived from any cellulose, hemicellulose, or lignin that has lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions that are at least 60 percent less than the baseline lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions.
2 Biomass-based diesel means a renewable fuel that has lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions that are at least 50 percent less than baseline lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions and meets all of the requirements of paragraph (1) of this definition:
-
- (1)(i) Is a transportation fuel, transportation fuel additive, heating oil, or jet fuel. (ii) Meets the definition of either biodiesel or non-ester renewable diesel. (iii) Is registered as a motor vehicle fuel or fuel additive under 40 CFR part 79, if the fuel or fuel additive is intended for use in a motor vehicle
- (2) Renewable fuel produced from renewable biomass that is co-processed with petroleum is not biomass-based diesel.
3 Advanced biofuel means renewable fuel, other than ethanol derived from cornstarch, that has lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions that are at least 50 percent less than baseline lifecycle greenhouse gas emissionsю.
4 Renewable fuel means a fuel that meets all the following requirements:
-
- (1)(i) Fuel that is produced either from renewable biomass or from a biointermediate produced from renewable biomass.
- (ii) Fuel that is used in the covered location to replace or reduce the quantity of fossil fuel present in a transportation fuel, heating oil, or jet fuel.
- (iii) Has lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions that are at least 20 percent less than baseline lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions, unless the fuel is exempt from this requirement pursuant to § 80.1403.
According to the definitions in Part 80 of the RFS, biogas means a mixture of biomethane, inert gases and impurities that meets all of the following requirements:
- It is produced by anaerobic digestion of renewable biomass according to approved technology.
- No non-renewable components added.
- It requires the removal of additional components to be suitable for its intended use (e.g. as a biointermediate for the production of renewable natural gas (RNG) or for the production of renewable fuels derived from biogas).
Renewable natural gas or RNG means a product which meets all the following requirements:
- It is derived from biogas that is produced from renewable biomass.
- It requires no additional impurities to be removed to be suitable for commercial distribution system.
- It is used for the renewable fuel production.
Biogas-derived renewable fuel means compressed or liquefied renewable natural gas (CNG/LNG) or any other renewable fuel that is produced from biogas or RNG, including the use of biogas as a biointermediate.
By the way, that EPA continues to consider the comments received on the proposed rulemaking to regulate the generation of Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs), which are RFS compliance credits, for transportation electricity generated from renewable biomass (eRINs). EPA will continue to work on possible ways to develop the eRIN programme.
You can read more about the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) Program on the EPA website.